
The IRS defines taxable income as the total amount of all income received in a year, less any allowable deductions. This is a bit more complicated than the simple definition of earned income because it includes all forms of income, even those that aren’t derived from your labor or business. For example, interest earned on bank and investment accounts, time deposits, savings bonds, canceled debt instruments, and other income are all considered taxable income by the IRS. Taxable income is based on adjusted gross income (AGI) minus allowable deductions.
Most of your taxable income will likely come from wages and salaries. These are reported on a W-2, which is sent to you by your employer. In addition, your employer withholds federal income taxes and FICA (Social Security and Medicare) taxes from your pay. Your taxable income may also include other forms of compensation, such as bonuses and stock options. Some types of unearned income are taxable, including royalty income from intellectual property, such as copyrights and patents, and rents from oil, gas, and mineral properties. Unearned income is generally reported on Schedule E, Supplemental Income and Loss, or Form 1040, Line 1.
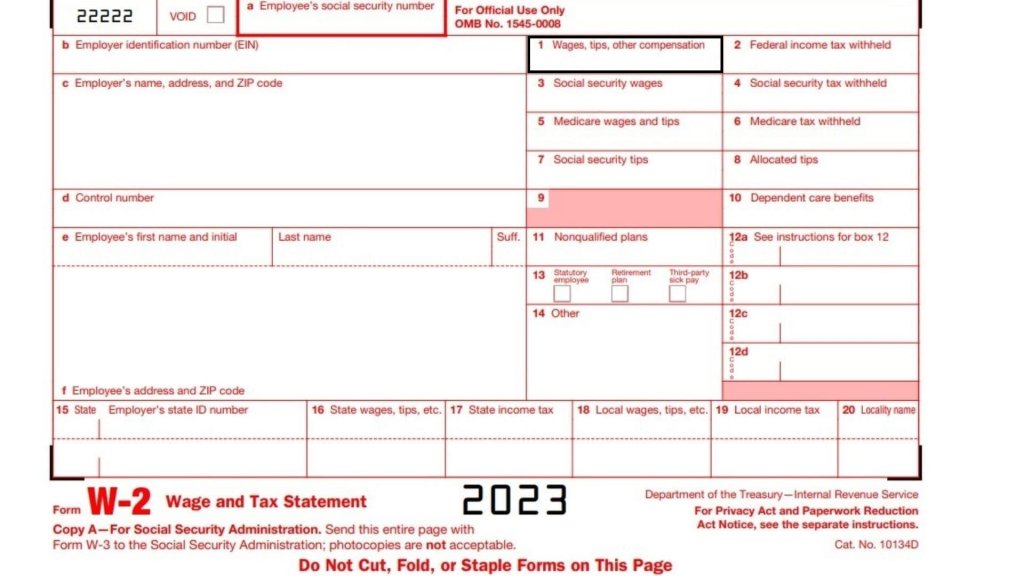
Taxable Income on Form W-2
Your employer’s W-2 Form shows your federal income taxable wage amount. It consists of your base salary plus any additional special payments or imputed income minus any salary reductions for pretax health insurance premiums or flexible spending account contributions.
- You can find your state and local taxable wages in box 1. Your taxable social security and Medicare wage amounts are reported in boxes 3 and 5. These wages include the same information as in box 1, except that the amount includes your federal income tax withheld for these taxes.
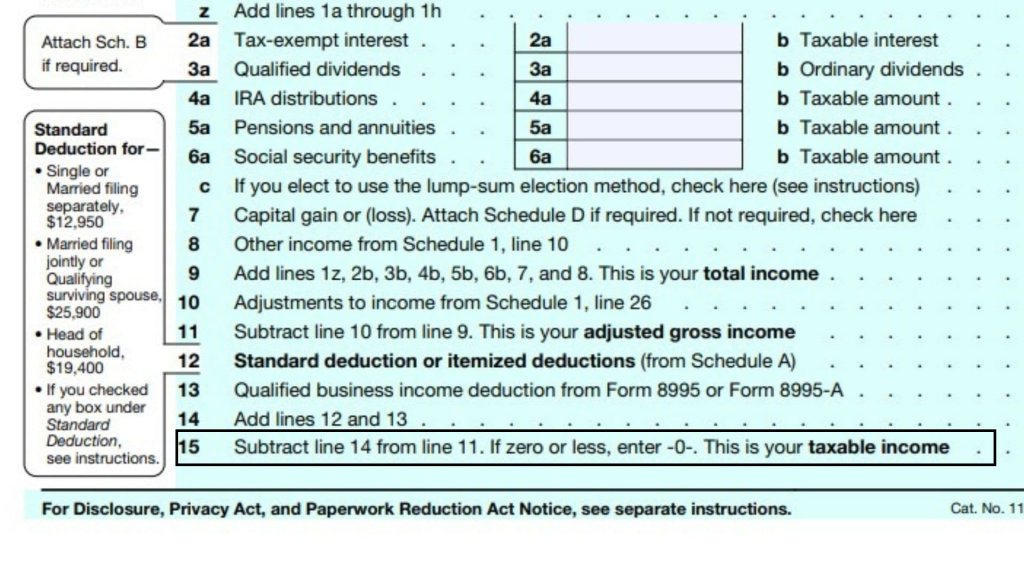
Taxable Income on Form 1040
The amount of taxable income you report on Form 1040 is the portion of your gross income that is subject to tax. It is calculated as your adjusted gross income (AGI) minus any applicable itemized deductions or standard deductions. Taxable income includes wages, salaries, tips, investment income, and certain other types of earned and unearned income. You can also deduct medical expenses, housing costs, state and local taxes, and charitable contributions. If you are self-employed, you can claim a qualified business income (QBI) deduction of up to 20% of your taxable income.
- When filling out Form 1040, Line 15 requires you to Subtract line 14 from Line 11. If zero or less, enter -0-. This is your taxable income.
How to Reduce Taxable Income?
Keeping track of all your earnings and expenses is key to making sure you get the most out of your tax benefits. There are ways to lower your taxable income before you file your taxes. For example, you can reduce your taxable income by making contributions to a retirement account, such as a 401(k) or an individual retirement account. You can also reduce it by claiming standard deductions or itemized deductions. Additionally, you can reduce your taxable income by investing in certain tax-free assets, such as municipal bonds and real estate. You can also reduce your taxable income by contributing to a flexible spending or health savings account.