
Filing taxes can be complex, but it is essential for all individuals, regardless of income level. As a low-income individual, understanding the tax system and taking advantage of available credits and deductions can significantly impact your financial well-being. This tax guide aims to provide the necessary information to navigate the tax process efficiently and maximize your tax benefits.
The taxation system in the United States is a complex structure that supports funding government operations and public services. The primary source of federal government revenue is the income tax, which is levied on individuals, businesses, and corporations based on their earnings. The tax rates vary depending on income brackets, with higher earners generally subject to higher tax rates. Additionally, the U.S. implements various other taxes, including payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare, excise taxes on specific goods and services, and estate and gift taxes.
State and local governments also impose their own taxes, such as sales taxes and property taxes, which contribute to funding local services and infrastructure. The U.S. taxation system involves a combination of progressive, regressive, and proportional tax elements, aiming to distribute the tax burden fairly across different income levels and support economic growth and public welfare.
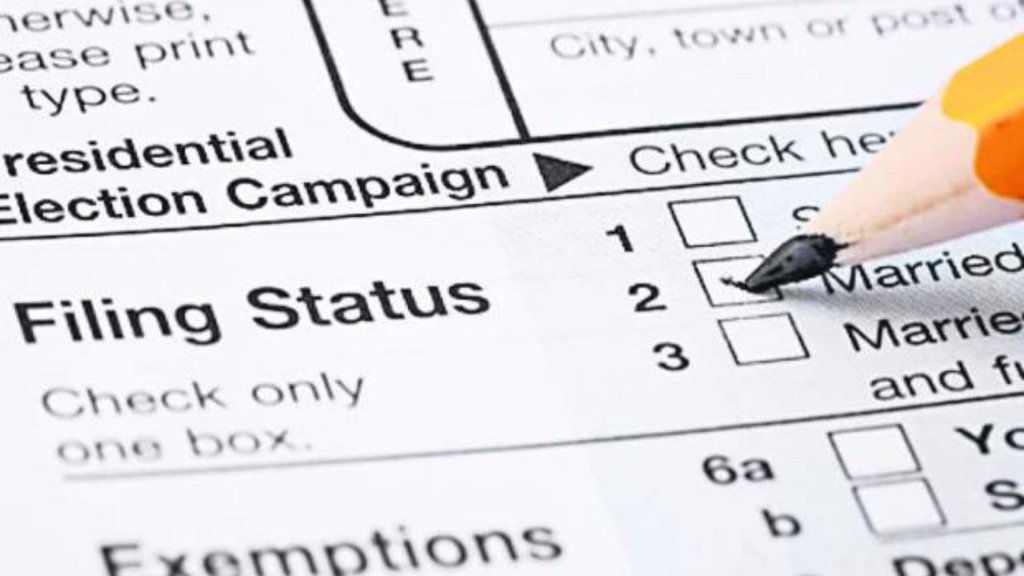
Determine Your Filing Status
Your filing status determines the tax rates, deductions, and credits available to you. As a low-income individual, you will likely fall into one of the following categories:
- Single: If you are unmarried, divorced, or legally separated.
- Head of Household: If you are unmarried, have dependents, and pay more than half of the household expenses.
- Married Filing Jointly: If you are married and wish to file a joint tax return with your spouse.
- Married Filing Separately: If you are married but want to file separate tax returns from your spouse.

Choose the Appropriate Tax Form
The form you use to file your taxes depends on your income level and filing status. The most common forms for low-income individuals are:
- Form 1040EZ: This is the simplest form and is suitable for single or married filing jointly taxpayers with no dependents and a taxable income below $100,000.
- Form 1040A: This form allows for more deductions and credits than Form 1040EZ and is appropriate if your taxable income is below $100,000 and you have dependents.
- Form 1040: If your income exceeds the limits of Form 1040EZ or Form 1040A, you will need to use Form 1040. This form provides the most extensive range of deductions and credits.

Deductions
Deductions help reduce your taxable income, potentially lowering the amount of tax you owe. Important deductions for low-income individuals include:
- Standard Deduction: You can claim the standard deduction if you don’t have enough qualifying expenses to itemize deductions. Note: The standard deduction increased significantly in recent years, so ensure you claim the correct amount for the tax year.
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC): The EITC is a refundable tax credit for low to moderate-income individuals and families. It can provide a significant boost to your refund if you qualify.
- Education Expenses: If you are pursuing higher education, you may be eligible for education-related deductions or credits, such as the American Opportunity Credit or the Lifetime Learning Credit.

Tax Credits
Tax credits directly reduce the amount of tax you owe and can sometimes result in a refund. Important tax credits for low-income individuals include:
Child Tax Credit: If you have qualifying children, you may be eligible for the Child Tax Credit, which can reduce your tax liability.
Savers Credit: If you contribute to a retirement account, such as an IRA or 401(k), and meet certain income requirements, you may be eligible for the Savers Credit.
Health Coverage Tax Credit: If you are receiving Trade Adjustment Assistance (TAA) or are a Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation (PBGC) pension recipient, you may qualify for the Health Coverage Tax Credit.

File Your Tax Return
Many low-income individuals can take advantage of free tax filing options. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides the Free File program, which offers free tax software for taxpayers with an income below a certain threshold.
Note: Be cautious of commercial tax preparation services that charge unnecessary fees, especially if you qualify for free filing.